Biological Molecules Enzymes . Biological catalysts are called enzymes, and the overwhelming majority of enzymes are proteins. (activated) coenzymes are small molecules. Enzymes are biological catalysts that catalyze more than 5000 different biochemical reactions taking place in all living. Enzymes are biological molecules (typically proteins) that significantly speed up the rate of virtually all of the chemical reactions that take place within cells. They cannot by themselves catalyze a reaction but they can help enzymes to do so. Enzyme, a catalyst that regulates the rate at which chemical reactions proceed in living organisms without itself being altered in the process. The exceptions are a class of rna molecules known as.
from mammothmemory.net
The exceptions are a class of rna molecules known as. (activated) coenzymes are small molecules. Enzymes are biological molecules (typically proteins) that significantly speed up the rate of virtually all of the chemical reactions that take place within cells. Enzyme, a catalyst that regulates the rate at which chemical reactions proceed in living organisms without itself being altered in the process. Enzymes are biological catalysts that catalyze more than 5000 different biochemical reactions taking place in all living. They cannot by themselves catalyze a reaction but they can help enzymes to do so. Biological catalysts are called enzymes, and the overwhelming majority of enzymes are proteins.
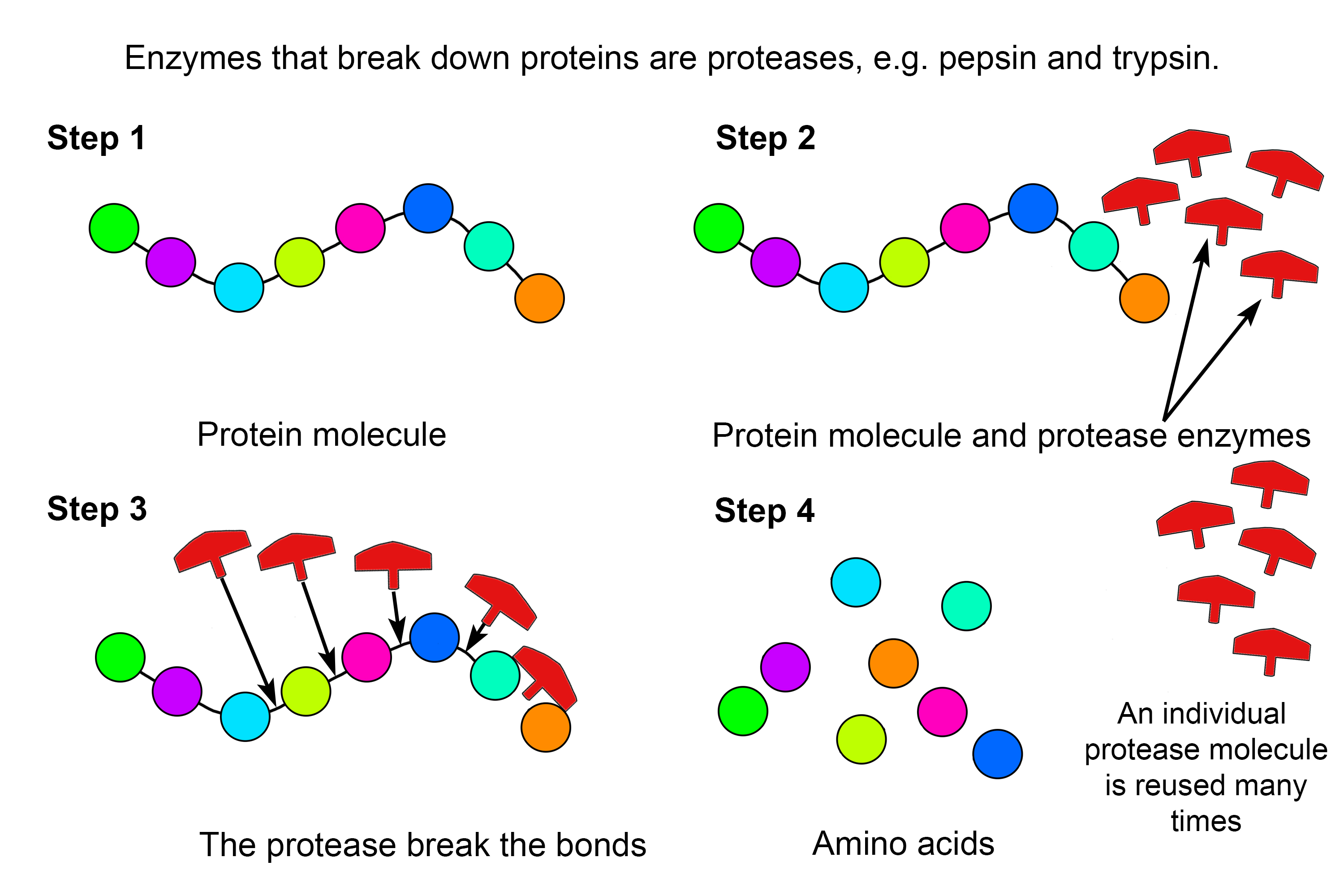
Example of how protease enzymes break down proteins
Biological Molecules Enzymes (activated) coenzymes are small molecules. Biological catalysts are called enzymes, and the overwhelming majority of enzymes are proteins. Enzymes are biological catalysts that catalyze more than 5000 different biochemical reactions taking place in all living. Enzymes are biological molecules (typically proteins) that significantly speed up the rate of virtually all of the chemical reactions that take place within cells. (activated) coenzymes are small molecules. The exceptions are a class of rna molecules known as. Enzyme, a catalyst that regulates the rate at which chemical reactions proceed in living organisms without itself being altered in the process. They cannot by themselves catalyze a reaction but they can help enzymes to do so.
From www.sciencelearn.org.nz
Digestive enzymes — Science Learning Hub Biological Molecules Enzymes Enzyme, a catalyst that regulates the rate at which chemical reactions proceed in living organisms without itself being altered in the process. Biological catalysts are called enzymes, and the overwhelming majority of enzymes are proteins. Enzymes are biological catalysts that catalyze more than 5000 different biochemical reactions taking place in all living. Enzymes are biological molecules (typically proteins) that significantly. Biological Molecules Enzymes.
From en.ppt-online.org
G11 Biology 20172018 Enzymes online presentation Biological Molecules Enzymes Biological catalysts are called enzymes, and the overwhelming majority of enzymes are proteins. The exceptions are a class of rna molecules known as. They cannot by themselves catalyze a reaction but they can help enzymes to do so. Enzymes are biological molecules (typically proteins) that significantly speed up the rate of virtually all of the chemical reactions that take place. Biological Molecules Enzymes.
From fity.club
Enzyme Biological Molecules Enzymes (activated) coenzymes are small molecules. The exceptions are a class of rna molecules known as. Enzymes are biological molecules (typically proteins) that significantly speed up the rate of virtually all of the chemical reactions that take place within cells. Biological catalysts are called enzymes, and the overwhelming majority of enzymes are proteins. Enzymes are biological catalysts that catalyze more than. Biological Molecules Enzymes.
From igbiologyy.blogspot.com
5.1. Enzymes Biology Notes for IGCSE 2014 & 2024 Biological Molecules Enzymes Biological catalysts are called enzymes, and the overwhelming majority of enzymes are proteins. The exceptions are a class of rna molecules known as. They cannot by themselves catalyze a reaction but they can help enzymes to do so. Enzymes are biological catalysts that catalyze more than 5000 different biochemical reactions taking place in all living. (activated) coenzymes are small molecules.. Biological Molecules Enzymes.
From www.abyntek.com
Enzymes for research types and applications Abyntek Biopharma Biological Molecules Enzymes Biological catalysts are called enzymes, and the overwhelming majority of enzymes are proteins. Enzymes are biological catalysts that catalyze more than 5000 different biochemical reactions taking place in all living. The exceptions are a class of rna molecules known as. They cannot by themselves catalyze a reaction but they can help enzymes to do so. (activated) coenzymes are small molecules.. Biological Molecules Enzymes.
From news.mit.edu
Scientists deliver highresolution glimpse of enzyme structure MIT Biological Molecules Enzymes Enzymes are biological catalysts that catalyze more than 5000 different biochemical reactions taking place in all living. The exceptions are a class of rna molecules known as. Enzyme, a catalyst that regulates the rate at which chemical reactions proceed in living organisms without itself being altered in the process. (activated) coenzymes are small molecules. Biological catalysts are called enzymes, and. Biological Molecules Enzymes.
From www.studocu.com
Biological Molecules and Enzymes EXERCISE 1 Biological Molecules and Biological Molecules Enzymes Biological catalysts are called enzymes, and the overwhelming majority of enzymes are proteins. Enzyme, a catalyst that regulates the rate at which chemical reactions proceed in living organisms without itself being altered in the process. Enzymes are biological molecules (typically proteins) that significantly speed up the rate of virtually all of the chemical reactions that take place within cells. They. Biological Molecules Enzymes.
From wordmint.com
Biological molecules and Enzymes Bingo Cards WordMint Biological Molecules Enzymes The exceptions are a class of rna molecules known as. Enzyme, a catalyst that regulates the rate at which chemical reactions proceed in living organisms without itself being altered in the process. Enzymes are biological molecules (typically proteins) that significantly speed up the rate of virtually all of the chemical reactions that take place within cells. Enzymes are biological catalysts. Biological Molecules Enzymes.
From www.thoughtco.com
Structure and Function of an Enzyme Biological Molecules Enzymes The exceptions are a class of rna molecules known as. Enzyme, a catalyst that regulates the rate at which chemical reactions proceed in living organisms without itself being altered in the process. (activated) coenzymes are small molecules. Enzymes are biological catalysts that catalyze more than 5000 different biochemical reactions taking place in all living. They cannot by themselves catalyze a. Biological Molecules Enzymes.
From www.slideshare.net
Session no. 2.2. biological molecules proteins and enzymes Biological Molecules Enzymes Enzymes are biological molecules (typically proteins) that significantly speed up the rate of virtually all of the chemical reactions that take place within cells. Biological catalysts are called enzymes, and the overwhelming majority of enzymes are proteins. (activated) coenzymes are small molecules. The exceptions are a class of rna molecules known as. They cannot by themselves catalyze a reaction but. Biological Molecules Enzymes.
From ibiologia.com
Enzymes Definition, Classification & Functions Biological Molecules Enzymes Biological catalysts are called enzymes, and the overwhelming majority of enzymes are proteins. Enzyme, a catalyst that regulates the rate at which chemical reactions proceed in living organisms without itself being altered in the process. Enzymes are biological catalysts that catalyze more than 5000 different biochemical reactions taking place in all living. Enzymes are biological molecules (typically proteins) that significantly. Biological Molecules Enzymes.
From www.youtube.com
General Biology 1 Components of an Enzyme YouTube Biological Molecules Enzymes Biological catalysts are called enzymes, and the overwhelming majority of enzymes are proteins. Enzyme, a catalyst that regulates the rate at which chemical reactions proceed in living organisms without itself being altered in the process. (activated) coenzymes are small molecules. Enzymes are biological molecules (typically proteins) that significantly speed up the rate of virtually all of the chemical reactions that. Biological Molecules Enzymes.
From edwardferserickson.blogspot.com
Are Enzymes Carbohydrates Lipids or Proteins Biological Molecules Enzymes (activated) coenzymes are small molecules. They cannot by themselves catalyze a reaction but they can help enzymes to do so. Enzymes are biological molecules (typically proteins) that significantly speed up the rate of virtually all of the chemical reactions that take place within cells. The exceptions are a class of rna molecules known as. Biological catalysts are called enzymes, and. Biological Molecules Enzymes.
From www.nagwa.com
Question Video Recalling the Group of Enzymes Which Amylase Belongs To Biological Molecules Enzymes They cannot by themselves catalyze a reaction but they can help enzymes to do so. The exceptions are a class of rna molecules known as. (activated) coenzymes are small molecules. Biological catalysts are called enzymes, and the overwhelming majority of enzymes are proteins. Enzyme, a catalyst that regulates the rate at which chemical reactions proceed in living organisms without itself. Biological Molecules Enzymes.
From pauldwoodfino.blob.core.windows.net
How Do Enzymes Their Function at pauldwoodfino blog Biological Molecules Enzymes Enzymes are biological molecules (typically proteins) that significantly speed up the rate of virtually all of the chemical reactions that take place within cells. Enzymes are biological catalysts that catalyze more than 5000 different biochemical reactions taking place in all living. Enzyme, a catalyst that regulates the rate at which chemical reactions proceed in living organisms without itself being altered. Biological Molecules Enzymes.
From msqbio11.blogspot.com
Grade 11 Chapter 4 ENZYMES Biological Molecules Enzymes Enzymes are biological molecules (typically proteins) that significantly speed up the rate of virtually all of the chemical reactions that take place within cells. Biological catalysts are called enzymes, and the overwhelming majority of enzymes are proteins. Enzyme, a catalyst that regulates the rate at which chemical reactions proceed in living organisms without itself being altered in the process. The. Biological Molecules Enzymes.
From www.livescience.com
How Do Enzymes Work? Live Science Biological Molecules Enzymes Biological catalysts are called enzymes, and the overwhelming majority of enzymes are proteins. (activated) coenzymes are small molecules. They cannot by themselves catalyze a reaction but they can help enzymes to do so. Enzyme, a catalyst that regulates the rate at which chemical reactions proceed in living organisms without itself being altered in the process. The exceptions are a class. Biological Molecules Enzymes.
From www.tes.com
Enzyme Basics (Structure and Function) AS Unit Biological Molecules Biological Molecules Enzymes (activated) coenzymes are small molecules. Enzymes are biological catalysts that catalyze more than 5000 different biochemical reactions taking place in all living. Enzyme, a catalyst that regulates the rate at which chemical reactions proceed in living organisms without itself being altered in the process. They cannot by themselves catalyze a reaction but they can help enzymes to do so. Biological. Biological Molecules Enzymes.